_________
/````````_\ S N I F ~ e2e TLS trust for IoT
/\ , / O\ ___
| | | \__|_____/ o\ e2e TLS SNI Forwarder
| | | ``/`````\___/ e2e TLS CA Proxy
| | | . | <"""""""~~
| \___/ `` \________/ https://snif.host
\ ''' ``` /```````` (C) 2021 VESvault Corp
\_________/
https://github.com/vesvault/snif
SNIF enables anonymous end-to-end public trust TLS communications between apps through a designated SNIF relay. By providing TLS public trust on a full end-to-end level, SNIF creates a peer-to-peer app-level VPN, eliminating the middle-man and any corresponding ability to intercept, monitor or read the private communication.
Any app on any device can utilize a designated SNIF relay to allow any other app on any device to directly communicate with the SNIF enabled app via a trusted, certificated and anonymous host name using full end-to-end TLS encryption.
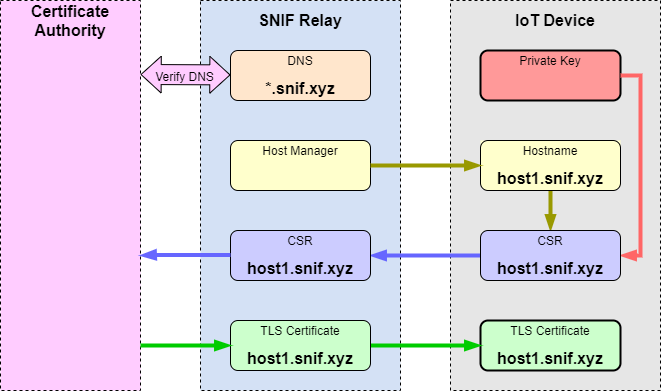
The private key is generated locally by the SNIF connector and never leaves the device.
The connector sends a CSR to the CA proxy on the SNIF relay server. The proxy acquires an X.509 certificate and feeds it back to the device.
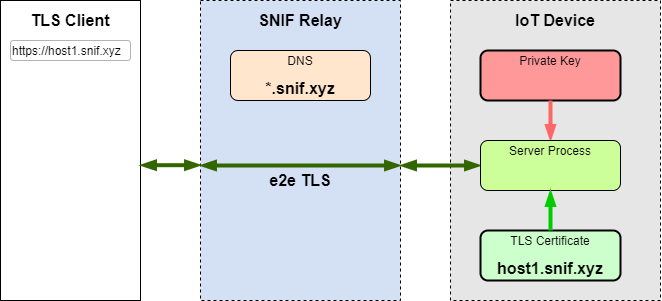
Having the certificate and the private key, the connector is now capable of terminating TLS traffic. Incoming TLS connections to the device's hostname come to the SNIF relay, which uses SNI record to identify the destination device and forward the TLS TCP socket traffic through the matching connector.
An IoT device can run snifd connector as a separate process that forwards incoming TLS connections to local ports, either unsecure TCP with TLS being terminated by snifd, or TLS being terminated by the listening app using the certificate and the private key shared with snifd.
In more advanced setups SNIF connector can be integrated directly with the app that serves incoming connections on the device.
From the client's point of view, a TLS connection to the hostname of the SNIF enabled device or app works same way as a TLS connection to a trusted server.
Any potential attempts of malicious actions by any SNIF relay are easily detectable through the public TLS certificate records.
To avoid public exposure of the unique SNIF hostname through the public CA records, the CA proxy can issue a wildcard certificate to a unique subdomain. The actual hostname will be a specific host within the certificate's subdomain that is not listed on the public records.
./configure
make
sudo make install
# Review settings in /etc/snif/snif.conf, edit the port mapping and other
# variables if necessary. The configuration defaults to the public SNIF
# Relay by VESvault, see https://snif.host#snif-pub.
snif-conn
# Follow the link the command outputs to authorize the certificate issuance
snif-conn
# Once authorization is complete, the command outputs the SNIF host name
# permanently assigned to this Connector.
# Configure the system to automatically launch snif-conn as a daemon with
# the argument '-d'. A systemd service file is included in this package, and
# is automatically installed in /lib/systemd/system if this path is available
systemctl enable snif-conn
systemctl start snif-conn
# Configure local TLS services mapped to SNIF ports to use the SNIF
# certificate and private key - /etc/snif/snif.crt, /etc/snif/snif.key
# For non-root processes, add the uid to group 'snif' to enable access
# to the files.
# Test the SNIF connection - check https://{snif_host_name}
# assuming that SNIF port 443 is mapped to the https server running on the
# device.
See ca-proxy/README for instructions
Use lib/cert.h to allocate the SNIF hostname, generate the private key, issue and renew the certificate.
Establish a SNIF Control Connection to {snif_host_name} on TCP port "snif" (7123).
Use lib/conn.h to receive and send SNIF messages over the control connection and to manage service connections.